The Maximal Oxygen Uptake – VO2max
The maximal oxygen uptake (VO2max) is - beside the anaerobic threshold - probably the most important and best-known parameter for the evaluation of endurance capacity.
VO2max indicates the maximum amount of oxygen the body can convert and describes the "size of the human engine". Oxygen uptake is usually measured in milliliters (ml) per minute (min) and expressed as an absolute (ml/min) or relative value (ml/min/kg).
Why Should I Know My VO2max?
- Understand how your performance capacity, especially your anaerobic threshold, is composed.
- Know your aerobic capacity to identify individual training zones and increase your VO2max through effective training.
- Evaluate your training progress and the strengths and weaknesses of your metabolic profile.
- Know your maximum aerobic capacity.
- Determine and understand your fat metabolism and carbohydrate consumption for effective training and pacing strategies.
Composition of VO2max
VO2max results from the interaction of different systems in the body. Simply put these are:
- the central cardiovascular system consisting of the heart, lungs, blood and blood vessels.
- the peripheral system of muscle cells and mitochondria.
VO2max is reached when all these systems are working at full capacity and working muscles are provided with the maximum available amount of oxygen. If VO2max is known, one knows the maximum amount of oxygen available for energy production during exercise.
What Does VO2max Mean?
VO2max stands for: Volume (V), strictly speaking a flow rate (V̇); O₂ stands for oxygen and max for maximum. Thus, VO2max is the metric that describes, how much oxygen reaches the mitochondria of muscle cells at a maximal rate. VO2max is considered the gross criterion of endurance performance because it represents the upper limit of aerobic capacity.
What Determines VO2max?
VO2max = Stroke volume (SV) x Heart rate (HR) x Arteriovenous Oxygen Difference (avDO2).
Stroke volume: defines the amount of blood ejected from the heart per heartbeat.
Heart rate: frequency of heartbeats per time interval.
Arteriovenous oxygen difference: the difference between the amount of oxygen transported to the muscle cells via the arterial blood and the amount returned from the muscle to the lungs via the venous system. The higher this difference, the more oxygen is available to the muscles for energy production.
The Importance of VO2max for Endurance Performance
The most important energy-producing system for cyclists, runners and triathletes is the aerobic metabolism. Here, with the help of oxygen (aerobic), glycogen and fatty acids are converted into energy. The parameter that describes the individual capacity of the aerobic system is the maximal oxygen uptake.
The aerobic system and its parameter VO2max can be used to evaluate and describe endurance performance. The higher the VO2max, the higher the capacity of the aerobic system for energy production and the higher the performance.
Compared to the anaerobic metabolism, the power that can be produced via the aerobic system is comparatively low; however, the duration of the achieved power output is much higher. In fact, the aerobic system can supply energy for hours and days, even during exercise.
Oxygen uptake increases proportionally to aerobic energy production, and VO2max describes a metric of aerobic performance. Therefore, the rule is easy for all endurance sports: The higher the VO2max, the better!
Good aerobic performance, along with an improved ability to break down lactate and metabolize it as an energy source, will lead to an improvement of the anaerobic threshold and endurance performance.
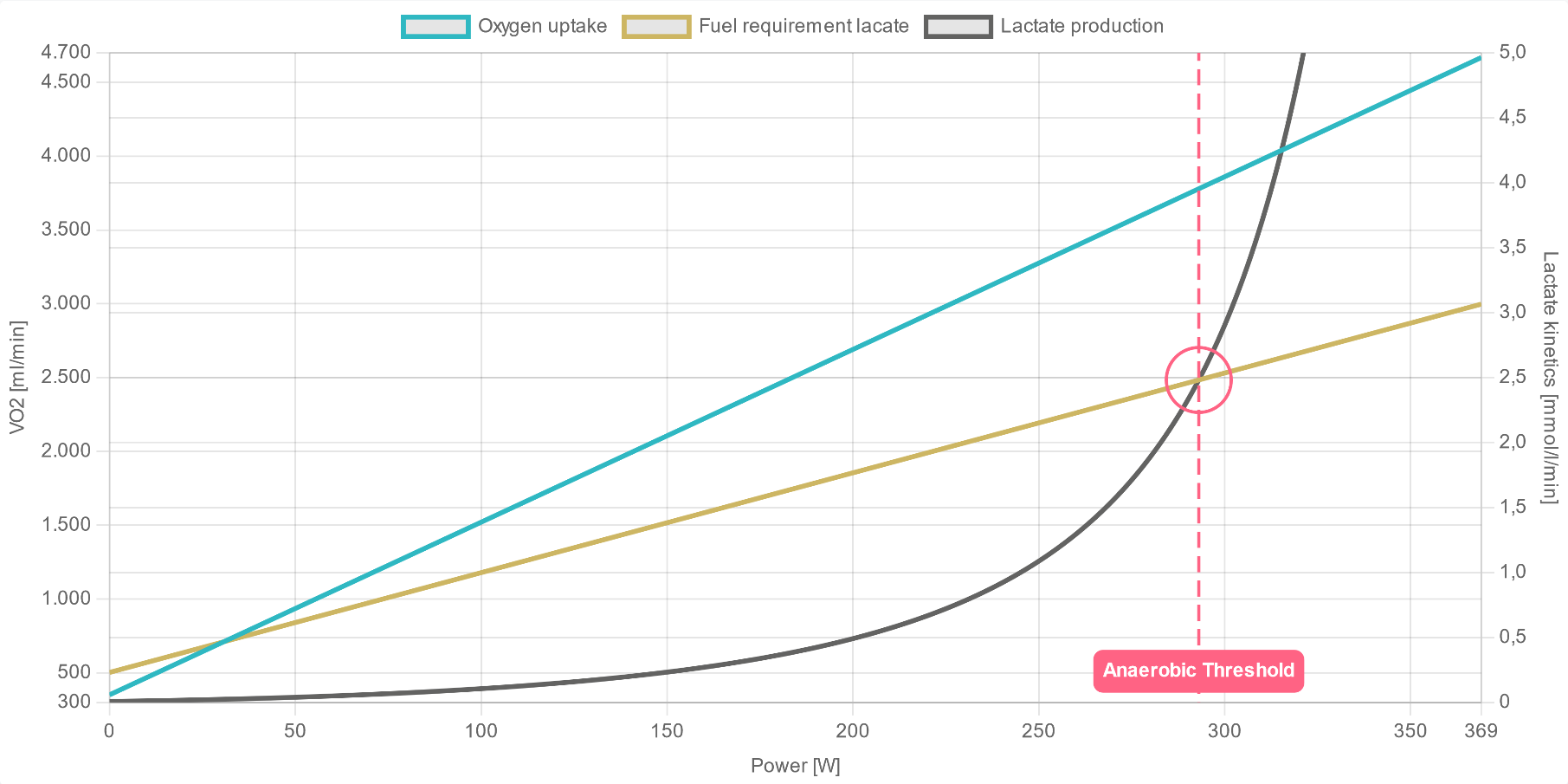
Metabolism diagram of an exemplary AI DIAGNOSTICS performance report
The Limiting Factor of the Aerobic System
The aerobic system is limited by the substrates to be metabolized, i.e., fats, carbohydrates, and proteins. Since fats are available in almost unlimited quantities and protein hardly plays a role in energy production during exercise, glycogen stores are the limiting factor.
If the glycogen reserves are depleted, an important substrate for energy production in the metabolism of aerobic energy production is missing and performance cannot be maintained, and power output must be reduced.
Power at VO2max
Your power at VO2max, also called maximal aerobic power, describes the power that can be achieved under maximum utilization of your aerobic system. For runners, cyclists, and triathletes, it often corresponds to the maximum 4- to 6-minute power output.
VO2max Metrics of an exemplary AI DIAGNOSTICS report
What Is a Good VO2max Value?
Reference Values for VO2max and Fitness in Endurance Sports
Since absolute VO2max (ml/min) does not take body mass into account, oxygen uptake relative to body mass (ml/min/kg) is used to compare and evaluate VO2max. In most endurance sports, relative VO2max is established as a comparative value.
The individual VO2max is mainly determined by the individual fitness level. Other factors are age, genetics, gender, and body composition. Thus, maximal oxygen uptake capacity decreases with age, and women achieve on average about 10% lower VO2max values than men.
Reference Values by Age and Gender
VO2max Guide Values for Men [ml/min/kg]
VO2max Guide Values for Women [ml/min/kg]
Reference Values by Performance Category and Gender
VO2max Guide Values for Men [ml/min/kg]
VO2max Guide Values for Women [ml/min/kg]
How to Determine VO2max?
The most accurate method for determining VO2max remains a performance diagnostic, including spiroergometry, in the lab. A standardized protocol is performed on an ergometer as a ramp test and respiratory gases (oxygen uptake and carbon dioxide exhaled) are measured in real-time. Using the respiratory gas analysis, the VO2max value is determined very accurately.
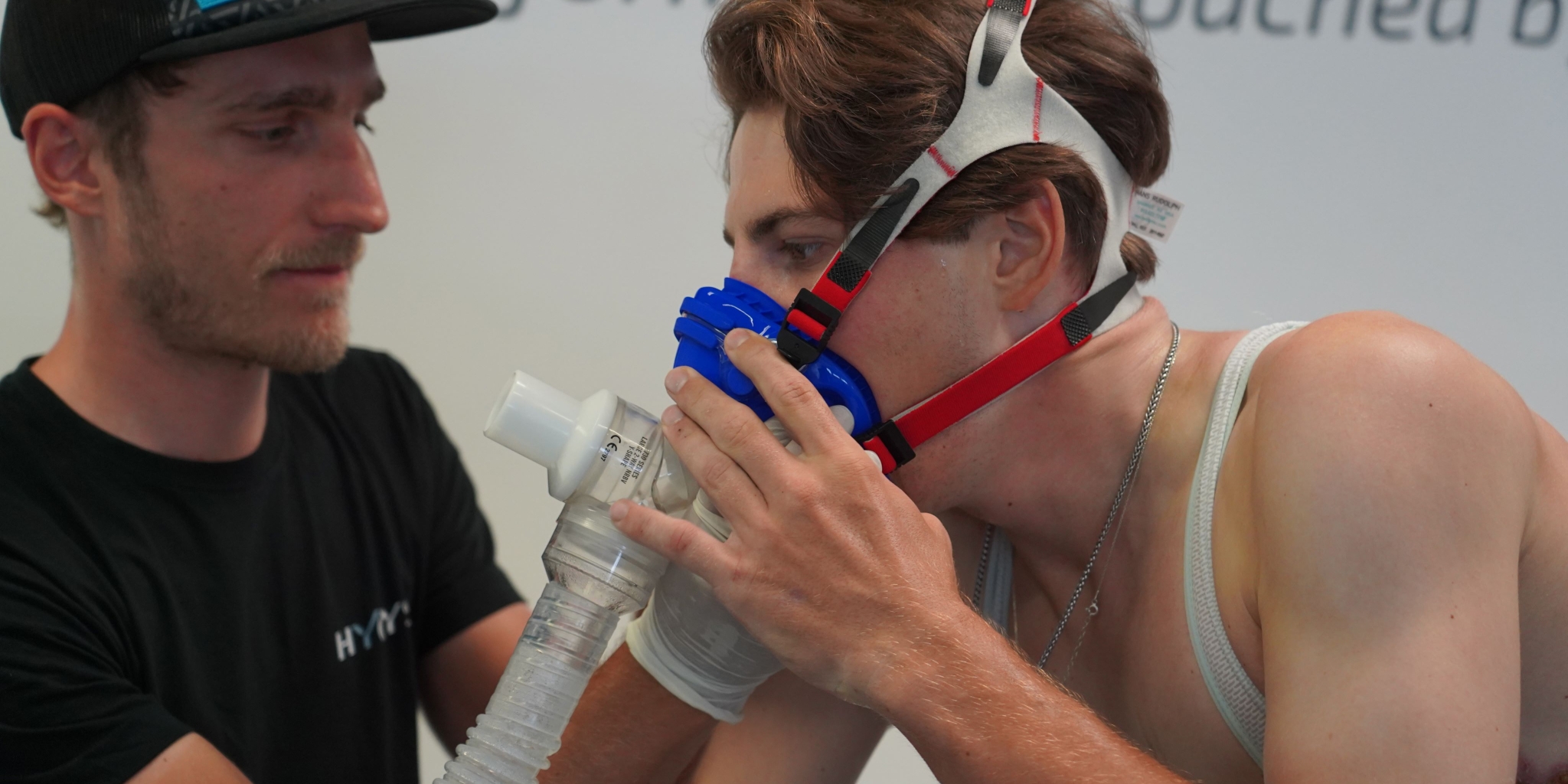

Spiroergometry under laboratory conditions to determine the maximum oxygen uptake VO2max
The procedure consisting of a ramp test and respiratory gas analysis is still considered the gold standard for determining maximum oxygen uptake.
Advantages of laboratory diagnostics: gold standard and most accurate method for determining VO2max.
The disadvantage of laboratory diagnostics: relatively time-consuming and expensive due to travel and visits to the laboratory.
Determine VO2max Easily and Cost-Effective from Home
AI DIAGNOSTICS allows to conduct a performance analysis simply at home to accurately determine VO2max. The test can be done on a smart trainer or "on the road".
Many alternative test methods, such as determining VO2max with modern sports watches, still fail to measure VO2max validly and reliably.
How Is the v02max Value Determined by AI DIAGNOSTICS?
Users benefit from years of experience and data from performance laboratories, as well as state-of-the-art methods in data science and machine learning. Hundreds of data sets are the basis of the AI DIAGNOSTICS methodology and allow to accurately determine VO2max even without a lab measurement.
For a valid analysis of the performance test, it is important to follow the AI DIAGNOSTICS test protocol.
How Fast Can You Improve VO2max?
First adaptations of the aerobic system and VO2max occur relatively quickly. Depending on the baseline level and training volume, the first improvements can be measured after 3 to 4 weeks. To achieve significant and measurable improvements, a training period of 6 to 8 weeks is needed. Regular VO2max tests are recommended to monitor the training progress.
VO2max Training
The trainability and maximum ceiling of your VO2max seems to be genetically determined. Thus, it is clear that not everyone can achieve a world-class VO2max of 80 to 90 ml/min/kg. However, an individualized training approach leads to significant improvements in VO2max and endurance performance in all athletes. High volume or high intensity? AI DIAGNOSTICS helps you to tailor your VO2max training based on your individual profile.